:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/difference-between-hill-and-mountain-4071583_FINAL-5c814b7646e0fb00018bd92d.png)
Differences Between Hills and Mountains
6. Saddle & Col. A saddle is literally that shape in the mountain that is high & broad at each end and narrower & lower in the middle. The saddle typically connects two mountains (or peaks). A Col is similar to a saddle but it always connects two peaks. Sometimes a Col is also understood as a saddle at high altitude.

Mountain Nomenclature Book Montessori, Montessori materials, Montessori geography
Definition: Alp. Arete - [French (arête) - edge or ridge] 1. A narrow ridge. 2. In glaciology, a narrow ridge remaining after glacial erosion from both sides. 3. In rock climbing, a vertical ridge or junction of walls at a convex angle in a rock face. Example: Arête. Barchan - [Kazakh] - An arc-shaped dune.

Montessori Materials Geography Classified A Mountain and its Parts Nomenclature Cards (Printed)
The different layers of the mountain. Mountains change as you go up them and these diagrams help demonstrate the different changes that you can see as you go up. The tree line is affected by a number of factors and so it can be found at 2000 metres in the Alps and at 2,700 metres in the Andes. The vegetation on the mountain has been classified.
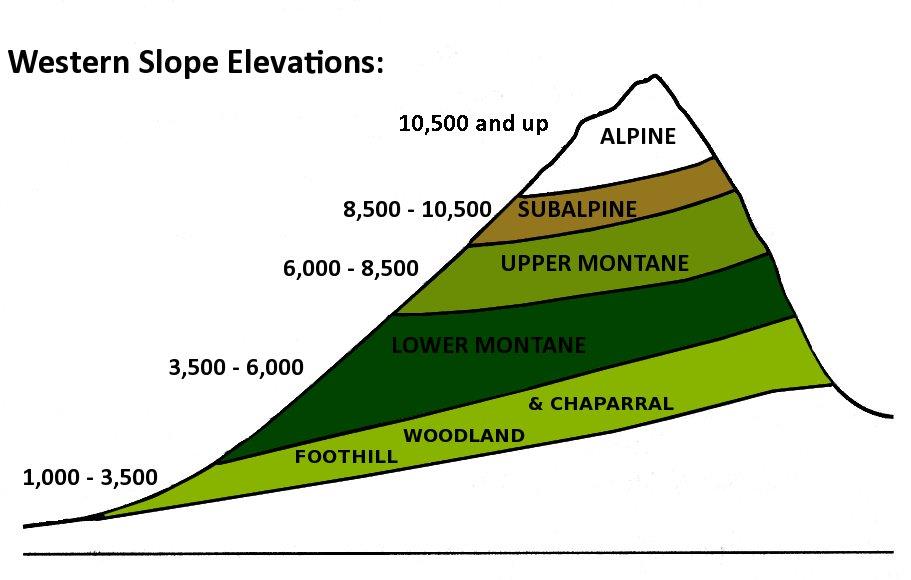
NCERT Summary Natural Vegetation 1 Notes EduRev
The Namcha Barwa Himal, east part of the Himalayas as seen from space by Apollo 9. A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have arisen from the same cause, usually an orogeny.
EDUCAT SOCIAL SCIENCE 3º
Answers for Part of a mountain range crossword clue, 6 letters. Search for crossword clues found in the Daily Celebrity, NY Times, Daily Mirror, Telegraph and major publications. Find clues for Part of a mountain range or most any crossword answer or clues for crossword answers.

Mountain diagrams
Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain. A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock.Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least 300 metres (980 ft) above the surrounding land.

Mountain Environments KS2 Planning Overview Teaching Resources
Science expert Emerald Robinson explains what a mountain is and how they form.Toview over 15,000 other how-to, DIY, and advice videos on any topic, visithttp.
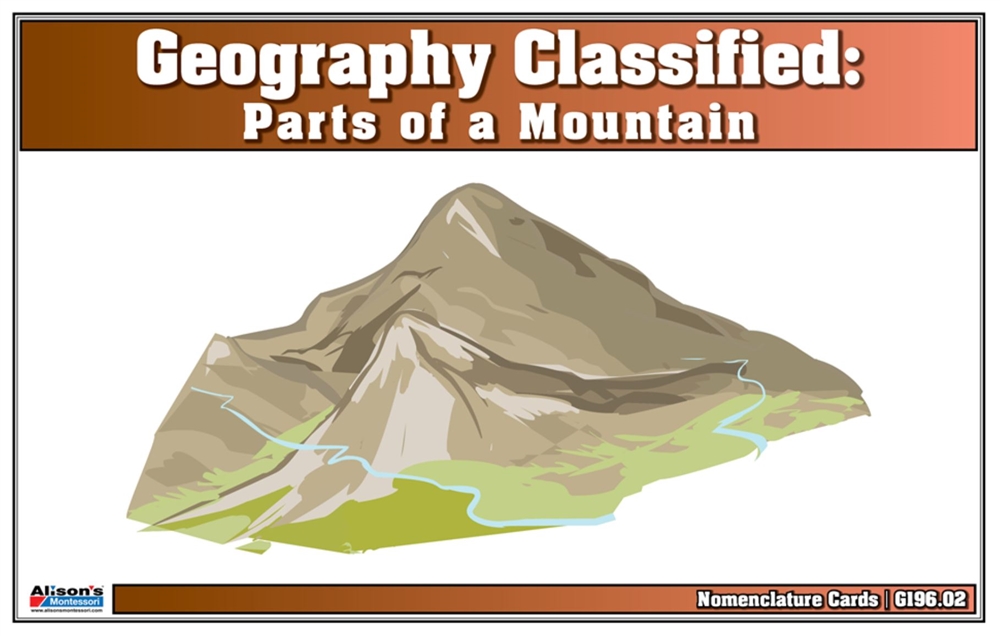
Parts Of A Mountain Nomenclature Cards Gambaran
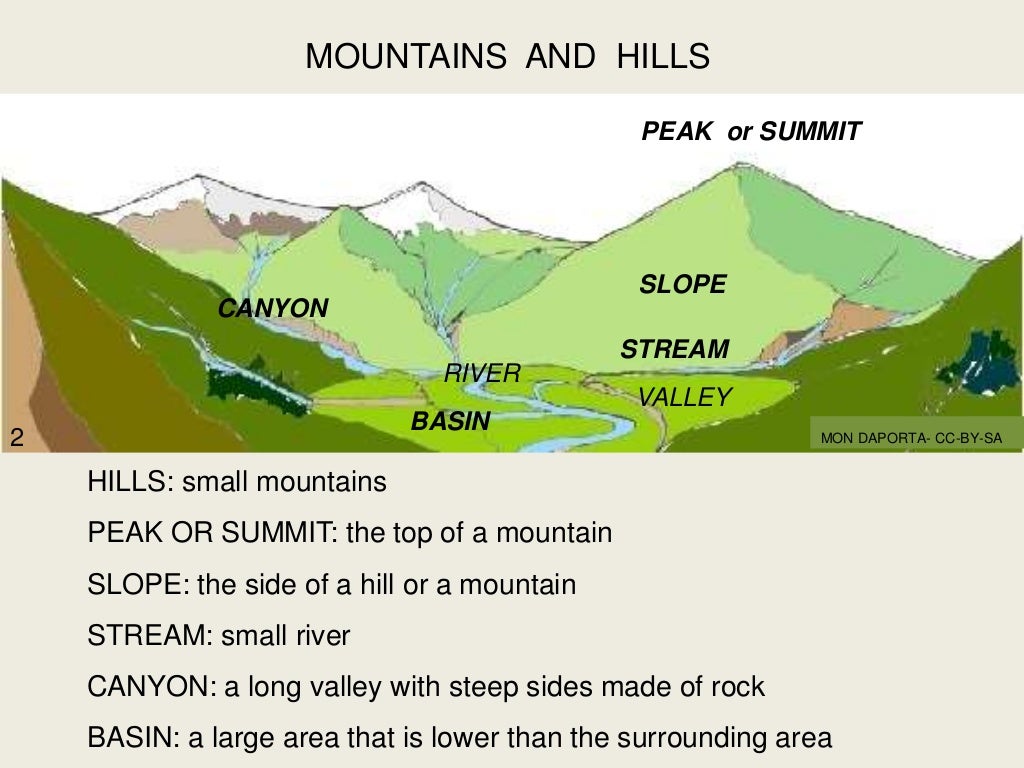
The top and highest part of a mountain is called the peak, or summit. The snow line is the place on the mountain above which snow can be found all year round. The slope is the side of the mountain. The slope reaches from the base to the peak. The base is the part of a mountain where the slope meets flat ground or hills.

Parts of a Mountain Mountain Topography Terms With Photos
Tires, inner tubes, and valves. Mountain bikes tend to have chunky tires for better grip. That said, smooth tires provide less rolling resistance and are better if you plan on doing miles on the road. The inner tubes hold the air that gives your tires their shape and firmness.
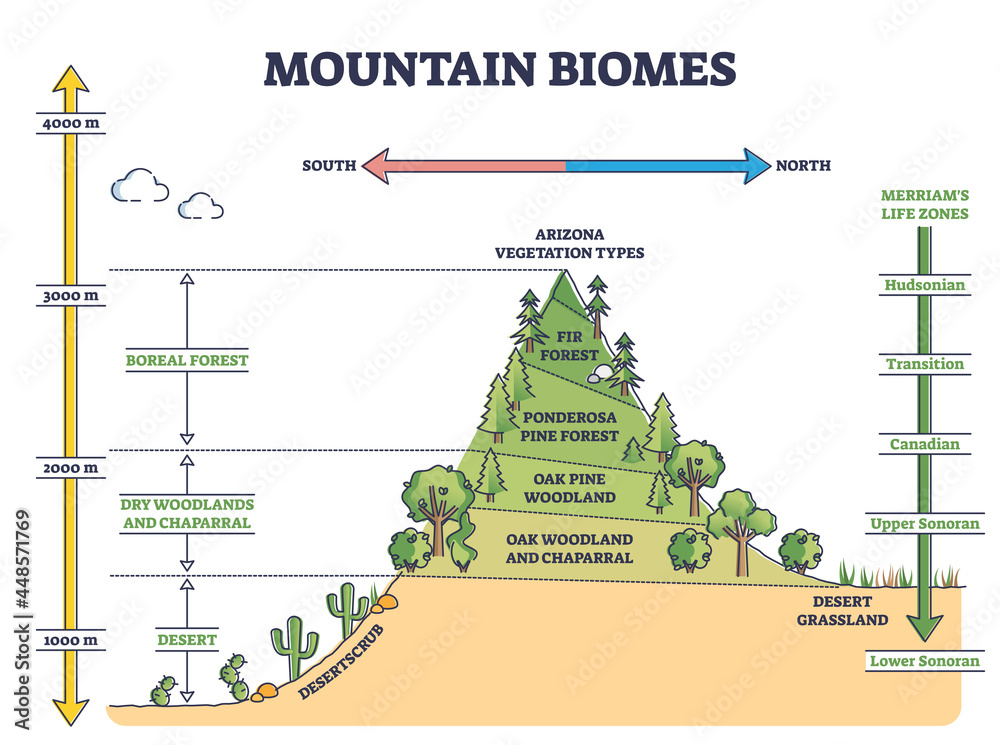
Mountain biomes with altitude and merriams life zones axis outline diagram. Educational climate
The summit of Mount Everest, at 29,035 feet (8,850 meters), is the highest point on Earth. The tallest mountain measured from top to bottom is Mauna Kea, an inactive volcano on the island of.
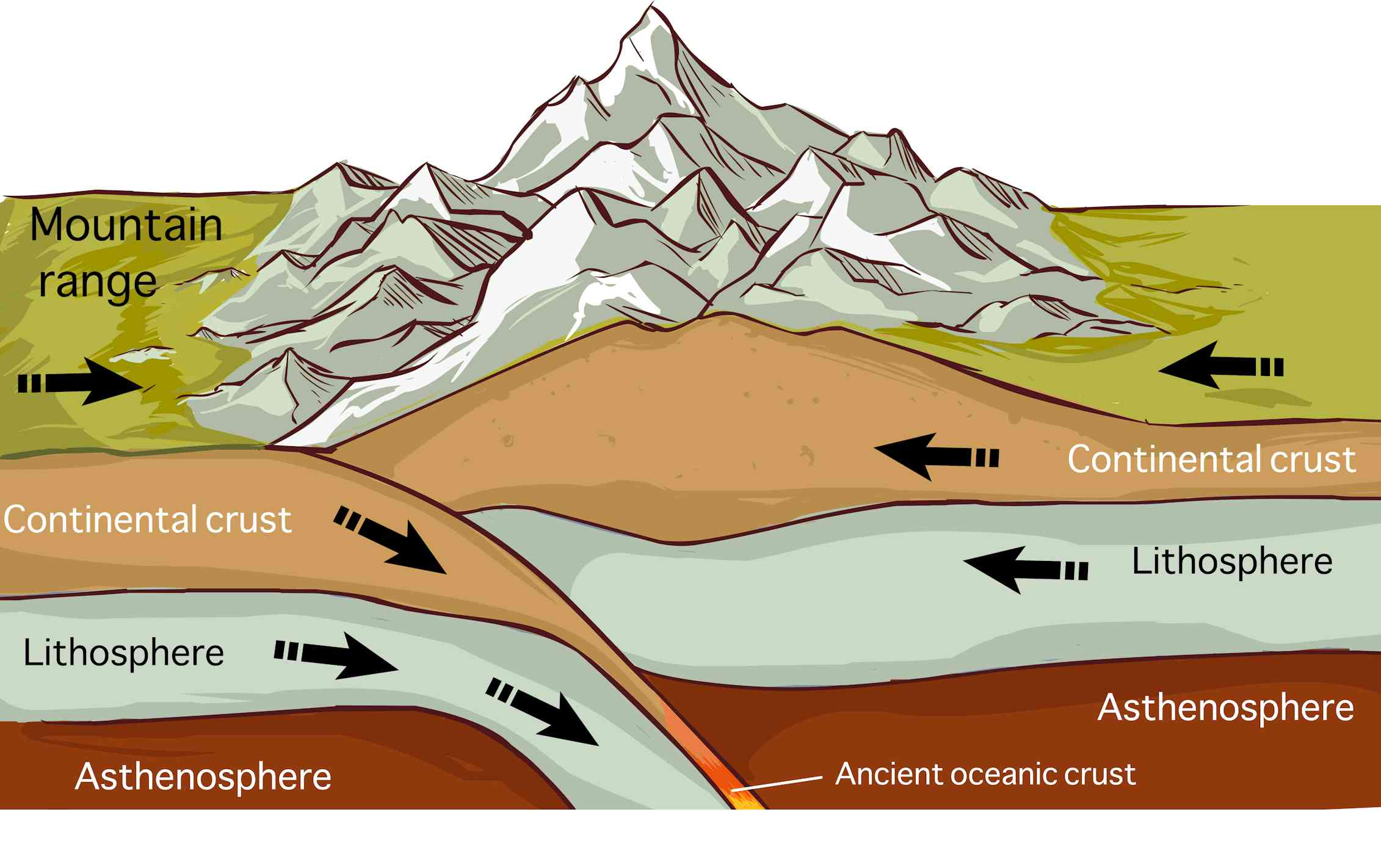
Curious Kids how do mountains form?
A mountain is made up of different parts. These are: Valley: is the terrain that lies between two mountains. Foot: the lowest part of the mountain, where the terrain begins to rise. Hillside or Skirt: the sloping part of the mountain between the foot and the top. Top: It is the highest part of the mountain.
Landforms
Col - low point on a ridge between to peaks. Saddle - a low point between two peaks. Used often for broader, flatter cols. Bluff - a steep slope or cliff. Peak - high point on a mountain or hill - may or may not be the summit. Summit - usually the highest point on a hill or mountain. Ravine - small steep valley. Gorge - steep-sided river valley.
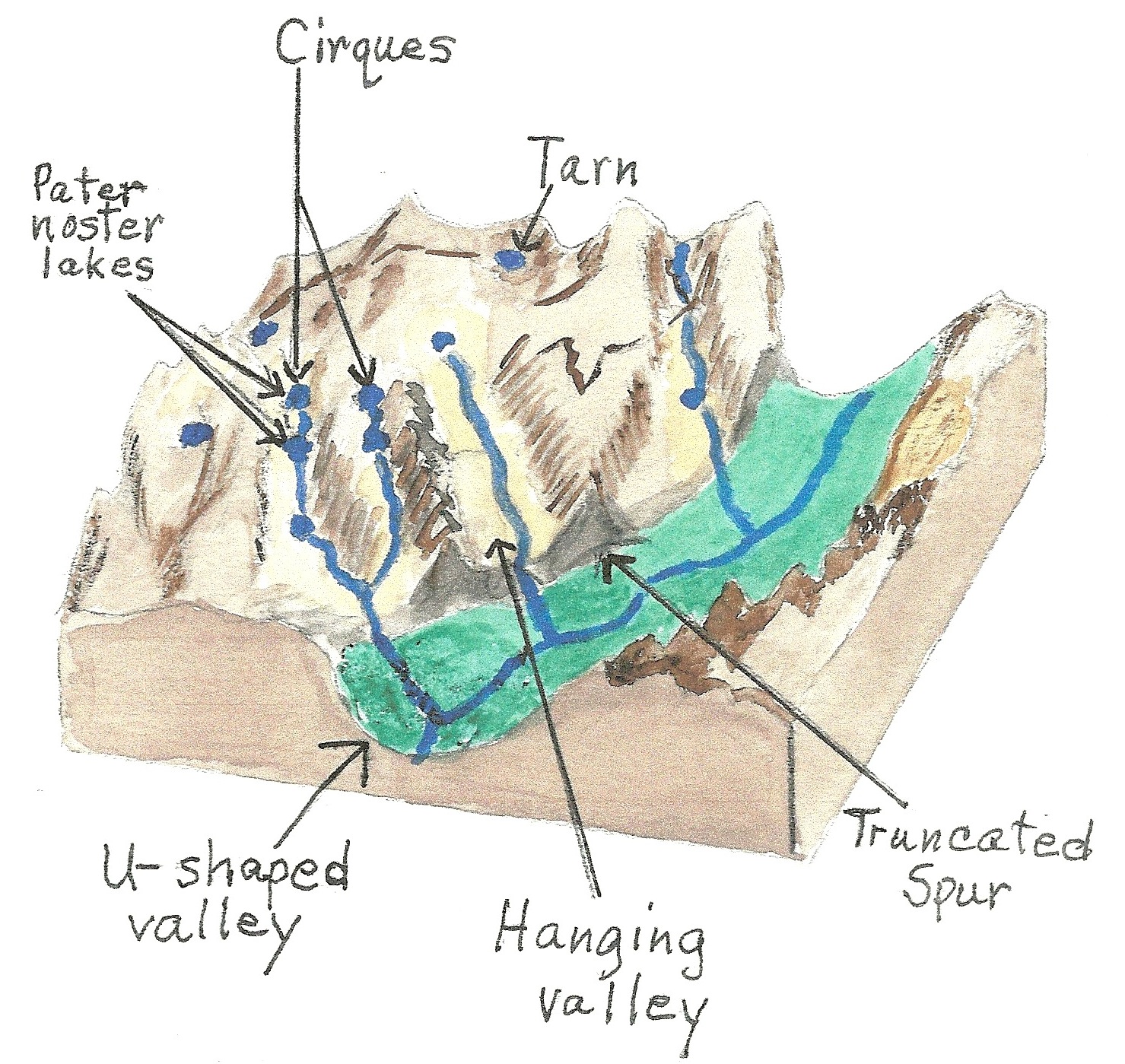
Glacier in the Rocky Mountains Definitions & Diagram Jake's Nature Blog
A mountain belt is many tens to hundreds of kilometres wide and hundreds to thousands of kilometres long. It stands above the surrounding surface, which may be a coastal plain, as along the western Andes in northern Chile, or a high plateau, as within and along the Plateau of Tibet in southwest China. Mountain ranges or chains extend tens to hundreds of kilometres in length.

Types and How Mountains are Formed For kids Owlcation
A top-down description of the parts of a mountain: Peak: The peak of a mountain is its highest pointed top. Summit: Highest measurable point on a mountain. Ridge: A long and narrow elevation of land. Snowline: The dividing line of the snow-covered and snow-free part of a mountain. A snowline can adjust seasonally and is formed due to the warmer.

Identifying the key features of mountains KS2 Teaching Resources
The Himalayas. Some well-known mountain ranges in the world include: the Himalayas in Asia, the tallest mountain range in the world. the Andes in South America, the longest range on land in the.

(A) Southwest face of the mountain Storvola (ca. 1 km high), showing... Download Scientific
mountain, Landform that rises well above its surroundings, generally exhibiting steep slopes, a relatively confined summit area, and considerable local relief (inequalities of elevation).Mountains are considered larger than hills, but the term has no standardized geologic meaning. Mountains are formed by the folding, faulting, or upwarping of the Earth's surface due to the movement of plates.
- Fundacion Plan B Educación Social
- Distancia A Complejo Asistencial Universitario De Burgos
- Objetivo Ojo De Pez Precio
- Material De Carpinteria De Segunda Mano
- Como Eliminar Bacterias Del Intestino
- Certificado De Delitos Sexuales Salamanca
- Fútbol Club Barcelona Manchester United
- Blusas Para Usar Con Palazzo
- Curso Control De Plagas Barcelona
- Toyota Aygo 1 0 Motor